Mining Investments
The world of mining investments is a complex and dynamic realm that plays a vital role in the global economy. To fully comprehend its significance, it is essential to first understand what mining investments entail. Mining investments refer to the financial backing provided for various activities related to extracting mineral resources from the earth’s crust, including exploration, development, production, and even reclamation.
Definition of mining investments
Mining investments encompass a wide range of financial arrangements made by individuals, corporations, governments, and other entities with an interest in leveraging the potential of mineral reserves. These investments can take various forms such as direct equity stakes in mining companies, purchases of mineral rights or royalties on production, funding for exploration projects or mine developments through debt financing or joint ventures.
Importance of mining investments in the global economy
Mining investments hold immense significance for economies worldwide. The extraction and utilization of mineral resources fuel economic growth and contribute to numerous sectors such as construction, manufacturing, energy production, and technology.
Mineral commodities like coal, iron ore, copper, gold, and rare earth metals are essential raw materials for industries around the globe. Moreover, mining projects generate employment opportunities while fostering infrastructure development in resource-rich regions.
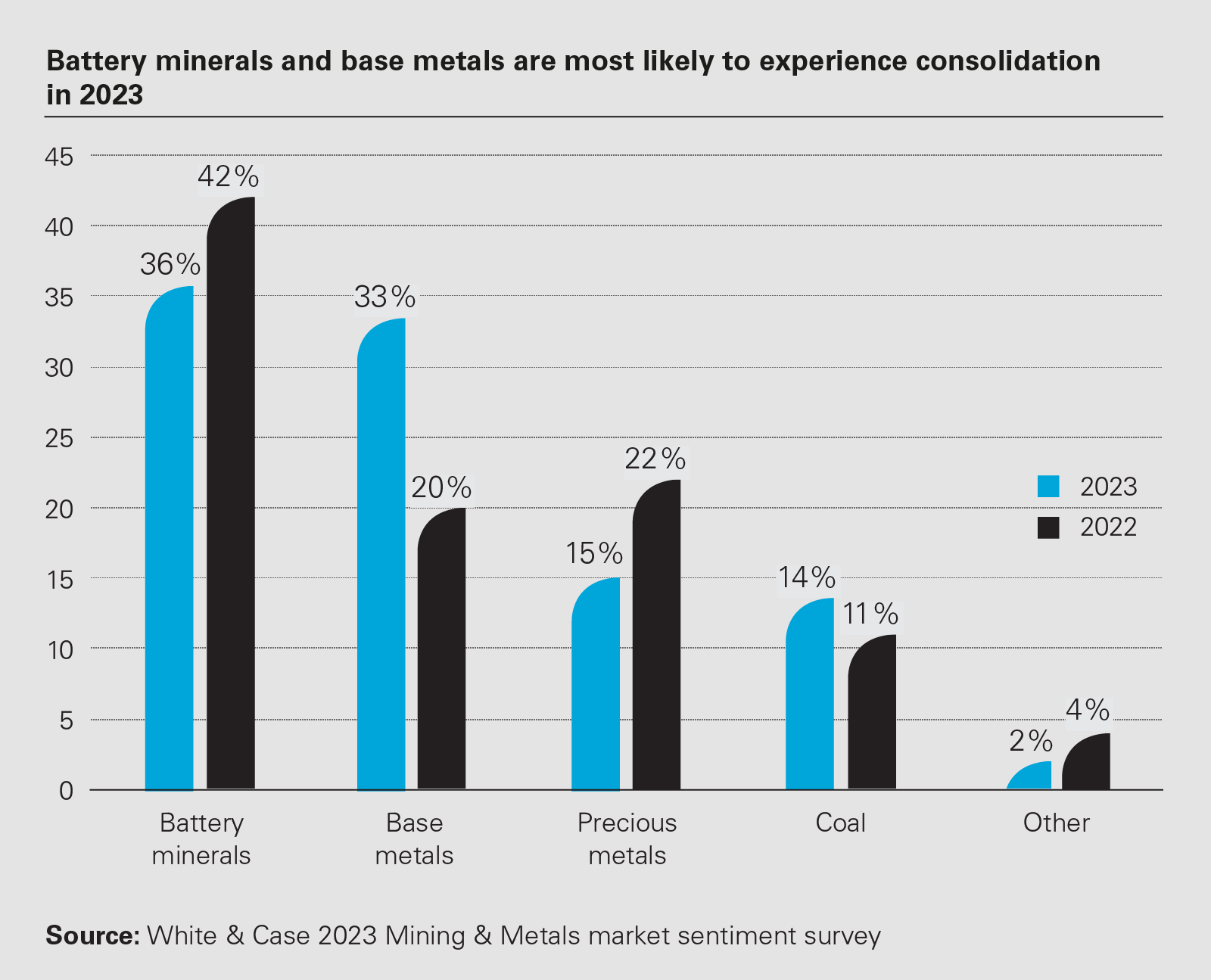
Overview of different types of mining investments
Understanding the diverse nature of mining investments is crucial for discerning investors seeking exposure to this sector. Various types of investment options exist at different stages within the lifecycle of a mine project:
- Exploration stage: investments at this stage focus on financing early-stage exploration projects aimed at identifying potential mineral deposits through geological surveys and prospecting techniques.
- Development stage: investment at this phase involves funding mine construction activities along with the procurement of essential infrastructure and equipment required for efficient operations.
- Production stage: Investments in producing mines aim to benefit from ongoing mineral extraction, processing, and sales. These investments can provide stable returns based on existing production and market conditions.
- Mine expansion or acquisition: investors may also consider opportunities to expand existing mines or acquire operational mines to capitalize on enhanced production capacity or favorable market conditions.
- Royalty and streaming agreements: alternative investment strategies include entering into royalty and streaming agreements, where investors provide capital upfront in exchange for a share in future production revenue without taking on the operational risks associated with mining activities.
By comprehending the intricacies of mining investments, investors can navigate this sector with more confidence, aligning their financial goals with the vast potential that lies within earth’s mineral resources. In subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into specific aspects of mining investments to offer a comprehensive understanding of this captivating realm.
Understanding the Mining Industry
The Evolution of Mining: Unearthing the Past for a Brighter Future
Mining, the process of extracting valuable minerals and geological materials from the Earth’s crust, has a rich and fascinating history that dates back thousands of years. From its humble beginnings when our ancestors used primitive tools to extract ores, minerals, and precious stones, mining has evolved into a complex and sophisticated industry. As societies progressed, so did mining techniques, with advancements in technology enabling more efficient extraction methods.
In ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Mesopotamia, mining was crucial for the development of robust economies and the creation of intricate infrastructures. Fast forward to modern times, mining plays an integral role in fueling economic growth worldwide.
Key Players Shaping Today’s Mining Industry
The mining industry comprises various stakeholders who contribute to its dynamic nature. At its core are the major players that shape the landscape through their significant operations and investments globally.
These companies possess vast resources, advanced technologies, and extensive expertise required to extract minerals from earth efficiently. Some notable names include BHP Billiton (Australia), Rio Tinto (UK/Australia), Vale S.A (Brazil), Glencore International AG (Switzerland), Anglo American Plc.
(UK/South Africa), and Freeport-McMoRan Inc.(USA). These formidable entities dominate global mineral production across diverse commodities such as iron ore, copper, coal, gold, silver among others.

Government Intervention: Balancing Interests for Sustainable Mining
The involvement of governments in mining projects is essential due to several reasons ranging from environmental concerns to economic development strategies. Governments play a critical role in crafting legislation related to mineral resource management which encompasses licensing procedures for exploration and extraction activities while ensuring compliance with safety regulations. They also establish policies aimed at facilitating investments in the sector, along with determining royalty rates and taxation frameworks.
Additionally, governments are often responsible for managing mining concessions, overseeing environmental impact assessments, and negotiating concession agreements with mining companies. This crucial interaction between governments and mining enterprises seeks to strike a balance between economic growth and sustainable resource management.
Factors Influencing Mining Investments
Geopolitical Considerations and their Impact on Investment Decisions
Subtitle: The Chessboard of Global Politics and Mining Investments Mining investments are significantly influenced by geopolitical considerations, as the interplay between nations shapes the investment landscape.
Political stability and conflicts impact the feasibility of mining projects, as unstable regions often pose inherent risks to investor interests. For instance, countries with a history of political unrest or corruption may deter potential investors due to concerns over the security of their investments.
Moreover, geopolitical tensions can lead to trade disputes or sanctions that affect mineral exports and imports, further impacting investment decisions. A comprehensive understanding of global politics is crucial for mining investors to navigate these complex dynamics.
Political Stability and Regulatory Frameworks in Different Countries
Subtitle: The Pillars of Investment Confidence in Mining Political stability is a fundamental prerequisite for attracting mining investments.
Governments play a vital role in creating an enabling environment through stable policies, transparent regulations, and effective governance structures. Countries with robust legal frameworks that protect property rights, enforce contracts fairly, and provide long-term policy certainty tend to attract greater investor confidence in the mining sector.
Regulatory frameworks should strike a balance between safeguarding environmental concerns while allowing sustainable extraction practices that contribute to economic growth. Investors carefully evaluate regulatory regimes before committing substantial financial resources to mining projects – they seek jurisdictions offering stability, predictability, and favorable investment conditions.

Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Practices Affecting Investments
Subtitle: Respecting Nature’s Bounty within Responsible Investment Practices In recent years, environmental regulations have become critical factors influencing mining investments due to increasing global awareness about sustainability issues. Governments worldwide are implementing stringent environmental standards to minimize the ecological impact of mining activities.
Investors now prioritize projects that adhere to sustainable practices such as land rehabilitation plans, water conservation measures, emission control strategies, and biodiversity preservation. The integration of environmental considerations into mining operations mitigates reputational risks, improves community relations, and enhances the long-term viability of investments.
Mining companies that demonstrate commitment to sustainable development attract environmentally conscious investors who recognize the importance of balancing economic prosperity with ecological preservation. Geopolitical considerations, political stability, regulatory frameworks, and environmental regulations all significantly influence mining investments.
The chessboard of global politics shapes investment decisions, as potential risks and opportunities exist in regions with different geopolitical dynamics. Political stability and transparent regulatory frameworks provide a solid foundation for investor confidence in the mining sector.
Furthermore, environmental regulations and sustainable practices have increasingly become key factors in investment decisions as investors prioritize projects that uphold ecological responsibility. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is essential for successful mining investments in an ever-evolving global landscape.
Exploration Stage Investments
During the exploration stage of mining investments, funding is primarily directed towards early-stage exploration projects. This involves conducting geological surveys and mapping techniques to identify potential mineral deposits. Geological surveys utilize sophisticated methods such as aerial photography, remote sensing, and satellite imagery to analyze terrain and identify geological structures that may contain valuable resources.
Mapping techniques help create detailed maps of prospective areas, aiding in the identification of potential mineral zones. In addition to geological surveys, prospecting methods like geochemical sampling and geophysical surveys are employed to assess the presence of minerals.
Geochemical sampling involves collecting rock or soil samples to determine their chemical composition, indicating the likelihood of valuable minerals being present. Geophysical surveys use various instruments to measure physical properties like magnetic fields or electrical conductivity, providing insights into subsurface structures that may contain minerals.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge the risks associated with exploration stage investments. The exploration process is inherently speculative and carries a high degree of uncertainty.
There is no guarantee that a project will yield economically viable deposits despite substantial investment in exploration activities. Factors such as geological complexities, geopolitical challenges, and unexpected environmental obstacles can significantly impact the success of exploration ventures.
Development Stage Investments
Once a promising mineral deposit has been identified through successful exploration efforts, development stage investments come into play. At this phase, funds are allocated towards financing mine construction, infrastructure development, and procurement of necessary equipment for efficient operations.
The capital expenditure requirements for developing a mine site encompass various elements such as land acquisition or leasing rights from local authorities or private landowners; constructing essential facilities like processing plants, workshops, accommodation units; setting up safety measures including ventilation systems and waste disposal facilities; establishing communication infrastructure; and implementing required environmental management plans. Infrastructure development plays a significant role in enabling smooth operations.
This involves building access roads to transport resources and equipment, establishing power supply lines to ensure uninterrupted operations, and creating water management systems to meet the mine’s requirements. Procurement of machinery, technology, and equipment is pivotal for efficient mining operations.
Heavy machinery like excavators, drills, haul trucks, crushers, and grinding mills are necessary for extracting minerals from the earth’s crust. Additionally, investing in advanced technologies such as automation systems or remote monitoring tools enhances productivity while adhering to safety standards.
Investment Strategies in Mining Sector
A: Traditional Investment Approaches
1: Direct equity investment in mining companies allows investors to acquire shares or stocks of specific mining companies listed on stock exchanges. This approach provides direct exposure to the performance and potential profits of the chosen company.
2: Investing through mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offers a diversified portfolio by pooling funds from multiple investors to invest in a range of mining companies. This approach spreads risk across various projects within the sector.
3: Participating in initial public offerings (IPOs) allows investors to buy shares of newly-listed mining companies at their inception stage. IPOs offer an opportunity for early entry into potentially lucrative ventures but carry higher risk compared to established companies.
B: Alternative Investment Strategies
1: Royalty streaming agreements involve providing upfront capital to mining companies in exchange for future royalties based on production revenue. This arrangement allows investors to indirectly benefit from successful mining operations without assuming operational risks.
2: Project financing involves providing loans or capital specifically for mining projects with structured repayment terms based on anticipated cash flows generated by the project itself. This strategy helps mitigate risks associated with exploration and development stages by aligning financial commitments with project milestones and profitability.
3: Joint ventures or partnerships with established miners enable investors to collaborate with experienced mining companies. These agreements offer access to operational expertise, shared resources, and reduced risk through shared costs and responsibilities.
Conclusion
The world of mining investments offers a vast array of opportunities for both traditional and alternative investment strategies. While exploration stage investments involve funding early-stage projects through geological surveys and prospecting methods, development stage investments focus on financing mine construction, infrastructure development, and equipment procurement. Traditional investment approaches include direct equity investment, mutual funds/ETFs, and participating in IPOs, while alternative strategies encompass royalty streaming agreements, project financing, and joint ventures/partnerships.
The mining sector presents the potential for substantial returns for those who navigate the risks intelligently and embrace diversification in their investment portfolio. By selecting high-quality projects backed by sound geological assessments and prudent financial management, investors can participate in this dynamic industry with confidence.
Amidst concerns about sustainability practices and environmental impact within the mining sector, responsible investors can also play a vital role by seeking out companies that demonstrate commitment to sustainable operations through ethical practices such as environmental stewardship, community engagement, and social responsibility initiatives. By supporting such initiatives through their investment choices, investors can contribute to a more sustainable future while enjoying potential financial rewards.




