The Quintessence of Precious Metals
Precious metals, a term that exudes a sense of opulence and rarity, refer to metallic elements that are highly valuable due to their scarcity, aesthetic allure, and significant industrial applications. This distinguished group primarily includes gold, silver, platinum, and palladium. These metals possess distinct characteristics such as high luster and shine, resistance to corrosion as well and oxidation which affirm their status as precious.
A Retrospective on Precious Metal Trading
Diving into the annals of history reveals that the trading of precious metals traces its origins back to ancient civilizations. Mesopotamia was likely the first civilization to engage in this practice around 3000 BC with rudimentary forms of gold bullion.
Silver also emerged as a popular medium of exchange in regions such as Lydia (modern-day Turkey) around 700 BC. The use of these metals extended far beyond ornamentation; they functioned as early forms of currency facilitating trade and showcasing wealth and power. Over centuries marked by imperial conquests and technological revolutions, precious metal trading evolved substantially yet retained its core essence. 
The Contemporary Significance: An Economic Cornerstone
In our contemporary global economy, precious metals continue to play an integral role; they serve not just as commodities but also as strategic financial assets. In times of economic instability or volatility in traditional markets like stocks or bonds, investors often turn towards these tangible stores of value for protection against inflation or currency depreciation – a phenomenon known as ‘flight-to-quality.’ Industries ranging from electronics to healthcare harness these metals for their unique properties while central banks amass them in reserves impacting national currencies’ strength. Precious metal trading is thus not a relic from the past but an active economic sphere embedded within our modern financial infrastructure providing opportunities for investment and speculation while contributing to global economic stability.
Understanding Precious Metals
The Quintessence of Valuable Resources
Precious metals, owing to their rarity and distinctive properties, have been held in high esteem since antiquity. They are natural occurring metallic elements that hold significant economic value.
Pivotal attributes such as resistance to corrosion and oxidation, coupled with their aesthetic appeal, distinguish them from common metals. Historically used as currencies, today they serve as crucial hedging instruments and investment assets.
Types of Precious Metals
Gold: The Immutable Asset
Gold is probably the most recognizable precious metal. Its lustrous yellow hue has captivated human interest for millennia.
Gold’s chemical symbol Au derives from the Latin ‘Aurum’, meaning ‘shining dawn’. It earns acclaim for its malleability, ductility, resistance to tarnish, and excellent conductivity of electricity.
Silver: The Luminary Metal
Silver or Argentum (Ag), renders a distinct lustrous white shine. Although more abundant than gold or platinum, it is highly prized for its reflectivity – the highest amongst all metals. Noted for its versatility and exceptional thermal conductivity, silver serves a multitude of industrial purposes.
Platinum: The Exquisite Element
Platinum (Pt) is coined as the ‘rich man’s version of gold‘. This dense, malleable metal exhibits a silvery-white appearance but is rarer than gold. Remarkably resistant to wear and tear and highly unreactive make platinum an ideal choice for jewelry making alongside other industrial applications.
Palladium: The Progressive Powerhouse
Palladium (Pd), another member of the platinum group metals (PGMs), often doesn’t receive much limelight but holds immense value in modern industries. It’s silvery-white metal, lighter than platinum but shares its resistant properties against corrosion and heat. 
Unique Characteristics of Each Metal
The Distinctive Allure
Each precious metal carries a unique set of characteristics that sets them apart. Gold, malleable and ductile, is also impervious to rust.
Silver’s reflectivity and superb electrical conductivity outshines all other elements. Platinum’s dense nature coupled with a high melting point renders it highly durable while Palladium’s ability to absorb large quantities of hydrogen at room temperature sets it apart.
Uses and Applications in Various Industries
The Versatile Virtuosi
The uses of these elements extend beyond the realm of jewelry or investment assets. Gold is usage in electronics due to its excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to tarnish. Silver, owing to its antibacterial properties, is used in medical applications as well as photovoltaic cells in solar panels.
Platinum serves crucial roles in catalytic converters for automobiles, hard disk drives and even cancer drugs due to its unreactive nature. Palladium has become indispensable in car manufacturing sectors due to its effectiveness as a catalyst in controlling harmful vehicle emissions.
The Glittering Market of Precious Metals
The global market for precious metals is a dazzling landscape, driven by myriad factors from industrial demand to investment strategies. It is an arena where the old and the new coexist – time-honored traditions of physical trading stand alongside digital platforms, and mining companies vie with recycling firms for their share of the supply. At its core, this market mirrors the broader shifts in our world economy, reflecting geopolitical tensions, technological advancements, and changes in consumer behavior.
Movers and Shakers: Key Players in the Metal Market
Several countries and companies play pivotal roles in shaping the precious metal market. On a national level, China holds sway as both a leading producer of gold and a significant consumer.
Other major players include Australia, Russia, and South Africa. On an institutional level, multinational corporations like Barrick Gold Corporation and Newmont Mining Corporation hold substantial influence over market dynamics.
A String Puller: The Role of Central Banks
Central banks play an instrumental role in precious metal trading by holding vast reserves (primarily gold), which they can buy or sell to stabilize their nation’s currency. Their policies can have far-reaching implications on metal prices worldwide. 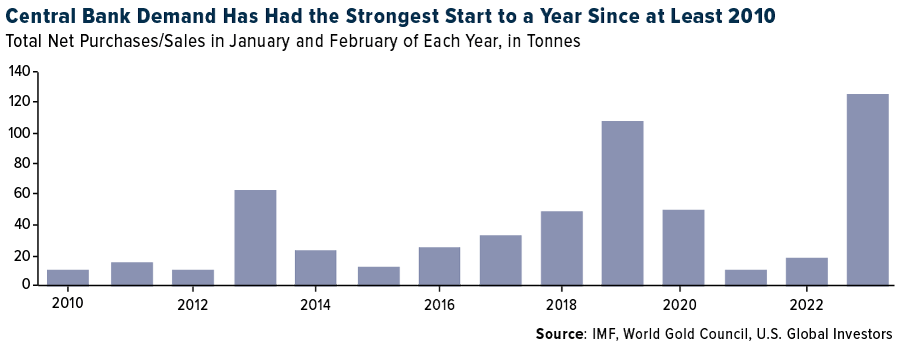
Unraveling Economic Threads: Factors Impacting Precious Metal Trading
Precious metals prices are influenced by a constellation of factors. Foremost among these are demand-supply dynamics; increased industrial usage or investment demand can drive prices upwards while oversupply can trigger price collapses.
Geopolitical Ripples on Golden Ponds
A tumultuous geopolitical event such as war or economic sanctions can cause uncertainty about future supply thereby causing price escalations.
Economic Indicators: Signposts in the Trading Landscape
Key economic indicators such as inflation rates, currency strength, and stock market performance can also influence precious metal prices. Typically, during times of economic instability, investors turn to gold as a ‘safe-haven’ asset.
Navigating Market Waves: Price Fluctuation and Volatility
The unpredictability of the factors influencing precious metal prices results in constant price fluctuation and volatility. Understanding these movements is crucial for both short-term traders looking to capitalize on price swings and long-term investors seeking stable returns.
Trading Instruments: Tools of the Trade
Physical vs Digital: A Tale of Two Trading Modes
Precious metal trading has traditionally involved physical transactions – buying, holding, and selling tangible assets. However, with advancements in technology, digital trading platforms have gained popularity owing to their convenience and accessibility.
A Golden Basket: Exchange-Traded Funds & Commodities
An increasingly popular instrument for precious metals investment is Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and commodities (ETCs). These financial products track the price of metals allowing investors to gain exposure without physically owning them.
Futures Contracts & Options: Speculating with Safety Nets
Futures contracts and options are derivative instruments that provide a way for traders to speculate on price movements while mitigating risk by locking in future buy or sell prices.
Safeguarding Fortunes: Risk Management in Precious Metal Trading
Like all forms of trading, precious metal investing carries certain risks – from changes in market sentiment to sudden regulatory shifts. Understanding these risks is paramount for successful trading strategies.
Illuminating Shadows: Unearthing Hidden Risks
Successful traders not only understand risks but also develop strategies to mitigate them. These can range from diversifying their investment portfolio, and utilizing hedging instruments, to keeping abreast of international events and policy changes.
Turning Metal into Gold: Case Studies on Successful Trades
Learning from successful trades is one of the best ways for new traders to understand the market. Such case studies reveal not just the decisions that led to profits, but also how risks were managed and opportunities seized upon.
Towards a Shiny Future: Upcoming Trends in Precious Metal Trading
The Digital Alchemy: Technological Impact on Trading
Technological advancements like Blockchain and AI are poised to revolutionize precious metal trading by enhancing transparency, reducing fraud and streamlining transactions. These changes will make trading more efficient and potentially even more profitable.
A New Frontier: The Potential of Space Mining
The potential influence of space mining on future supply is an exciting development. While still in its nascent stages, it could radically alter the supply dynamics in future decades while fostering a whole new era of exploration and discovery.
The Golden Thread that Weaves Our World Together
Precious metal trading is a fascinating arena that merges finance, economics, technology, and even geopolitics. It offers ample opportunities for both seasoned investors and enthusiastic beginners.
As we look forward to a future where digital innovations meet cosmic aspirations, it’s clear that the allure of precious metals will continue to glitter brightly in our global economy. This dynamic field welcomes you with open arms – whether you seek further study or active participation




