The price of gold has soared to unprecedented heights, reaching the highest gold spot price ever recorded. At an astounding $2,160 per troy ounce, this surpasses the previous record of $2,135 per troy ounce. The surge in gold prices can be attributed to a combination of factors, including economic and geopolitical uncertainty.
One contributing factor to the increase in gold prices is the weakening value of the U.S. dollar. As the dollar loses strength, investors turn to alternative assets such as gold to preserve their wealth and hedge against inflation. Additionally, optimism about U.S. monetary policy has further fueled the rise in gold prices. Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell recently hinted at possible interest rate cuts, generating even more interest in the precious metal. In fact, the probability of the central bank cutting rates at its June meeting is as high as 73.9%.
Geopolitical conflicts around the world have also had a significant impact on the surge in gold prices. Lingering tensions and uncertainty surrounding conflicts, such as the wars in Ukraine and Gaza, have driven up investor demand for gold as a safe haven. Furthermore, central banks, particularly China, have been increasing their gold reserves since 2022, leading to heightened demand for the precious metal.
This remarkable increase in gold prices presents a unique opportunity for investors. By capitalizing on this upward trend, investors have the potential to reap significant rewards. To navigate this promising market, it is crucial to stay informed and make informed decisions based on expert analysis and market trends.
For more insights into the factors driving the surge in gold prices and strategies for investing in this lucrative market, please refer to this CNBC article.
Don’t miss out on this historic opportunity, take advantage of the highest gold spot price ever and reach new riches!
Impact of Federal Reserve’s Policy on Gold Prices
When it comes to understanding the fluctuations in gold prices, one cannot ignore the significant role played by the Federal Reserve. As the central bank of the United States, the Federal Reserve’s policy decisions have a direct impact on the economy as well as various financial markets, including the gold market.
Gold prices tend to have an inverse correlation with the value of the U.S. dollar. This means that when the dollar weakens, gold prices tend to rise, and vice versa. One of the key factors influencing the value of the dollar is the Federal Reserve’s stance on interest rates.
The Federal Reserve’s ambiguity about interest rate cuts has weakened the dollar in recent times, leading to a rise in gold prices. Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell has clarified that interest rate cuts will be possible “at some point this year.” History shows that when interest rates are lowered, it typically results in higher gold prices.
Currently, the CME Group’s FedWatch Tool indicates a high probability of the central bank cutting rates at its June meeting. This anticipated rate cut could serve as a catalyst for a further increase in gold prices.
As investors closely monitor the Federal Reserve’s policy decisions, any hints or changes in interest rates can have a significant impact on the gold market. It is essential to stay informed about the Federal Reserve’s actions and their potential effects on gold prices.
In summary, the Federal Reserve’s policy decisions, particularly regarding interest rates, play a crucial role in determining the direction of gold prices. As the financial markets closely watch for any changes in the Federal Reserve’s stance, investors should stay informed to make well-informed decisions regarding gold investments.
Continue to learn more about the history of the Federal Reserve’s impact on gold prices.
Factors Contributing to the Increase in Gold Prices
The recent rise in gold prices can be attributed to various factors.
Firstly, the decline in the 10-year Treasury yield has made gold a more attractive investment compared to Treasury notes.
The uncertainty in global markets due to geopolitical conflicts, such as the wars in Ukraine and Gaza, has also led to increased investor demand for gold as a safe haven.
Additionally, central banks, especially China, have been buying gold since 2022, which has driven up demand for the precious metal.
The rise in gold prices due to these factors highlights the importance of considering gold as an investment option in times of economic uncertainties.
Considerations for Investors Buying Gold
When it comes to building a robust investment portfolio, diversification is key. One asset that often comes to mind is gold. Investing in gold can offer potential gains and act as a store of value, but it’s essential to consider certain factors before diving in.
Financial advisors typically recommend allocating no more than 5-10% of one’s total investment portfolio to gold. This percentage allows for diversification without overly exposing one’s portfolio to the risks associated with gold.
Before deciding to buy gold, it’s important to understand the potential risks involved. Gold prices are influenced by various economic factors, such as inflation readings and job numbers. These factors can cause fluctuations in the price of gold, impacting its value within an investor’s portfolio.
However, it’s important to note that gold’s value has historically shown resilience during economic uncertainties. This quality is what makes it attractive for investors seeking to safeguard their investments.
When considering adding gold to an investment portfolio, it is crucial to evaluate personal investing preferences and financial goals. Each investor’s circumstances and risk tolerance are unique, and understanding these factors will guide the decision-making process.
There are different approaches to invest in gold. Long-term investors often prefer purchasing physical gold, such as bullion or coins, as it allows for direct ownership and possession of the precious metal. Another option is investing in gold miner stocks, which provide exposure to the gold industry’s potential growth. Additionally, gold-leveraged exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offer a way to participate in the gold market through shares of funds that track the price of gold.
Understanding the potential benefits and risks of investing in gold is essential when exploring this asset class. By exercising prudence and considering the diversification needs of a portfolio, investors can make informed decisions regarding the inclusion of gold in their investment strategy.
For further research on the relevance of gold as a strategic asset, explore the resources provided by the World Gold Council.
Historical Fluctuations in Gold Prices
Over the past century, gold prices have experienced significant fluctuations, demonstrating the dynamic nature of the precious metal market. Historical data indicates that gold prices have exhibited large swings in both directions, influenced by various economic and geopolitical factors.
Factors such as inflation, geopolitical tensions, supply and demand dynamics, and mining and refining costs play a crucial role in shaping the price trends of gold. Understanding these factors can help investors gain insights into the patterns and trends that have historically impacted the price of gold.
Analyzing long-term data provides valuable information about gold price fluctuations. However, it’s important to note that past performance does not guarantee future results.
In 1980, gold reached its highest inflation-adjusted price, surpassing the peak reached in 2024 in nominal terms. These milestones highlight the significance of considering inflation-adjusted prices when evaluating the historical performance of gold.
To illustrate the significance of historical fluctuations in gold prices, consider the  . The visual representation of price trends showcases the dynamic nature of gold prices over time and the potential opportunities it offers to investors.
. The visual representation of price trends showcases the dynamic nature of gold prices over time and the potential opportunities it offers to investors.
- Inflation: Changes in inflation rates can impact the value of currency, which in turn affects the demand for gold as a hedge against inflation.
- Geopolitical tensions: Political conflicts and uncertainties on a global scale can lead investors to seek the stability and perceived value of gold, driving up its price.
- Supply and demand: The availability of gold and its demand in various industries and investment sectors can influence its price.
- Mining and refining costs: The cost of extracting, refining, and producing gold affects its overall price, as higher production costs can result in higher prices.
Investors looking to make informed decisions about investing in gold should consider these historical price fluctuations and the key factors that have influenced them. Additionally, seeking guidance from financial professionals can help individuals navigate the complexities of the gold market and develop strategies that align with their investment goals.
Comparison of Gold and S&P 500 Over Time
When it comes to comparing investments, it’s essential to evaluate the performance of different assets over time. In the case of gold, which is often considered a safe haven during economic uncertainties, comparing its performance with the S&P 500, a standard metric for stocks, can provide valuable insights.
Historically, gold has served as a reliable store of value during times of economic uncertainty and market volatility. While the S&P 500 has experienced both short-term fluctuations and long-term growth, gold has stood the test of time as a tangible asset.
When analyzing the performance of gold and the S&P 500 over different periods, it’s crucial to consider the specific economic and geopolitical conditions that influenced their respective values. Factors such as inflation rates, interest rates, fiscal policies, and global events can all impact the performance of these investments.
It’s worth noting that the value of gold and the S&P 500 can be influenced by a variety of factors, including market sentiment, investor behavior, and macroeconomic indicators. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results, and it’s important to exercise caution when drawing conclusions based solely on historical data.
To gain a deeper understanding of the relationship between gold and the S&P 500, investors can analyze price trends, correlations, and market dynamics. Researching the historical performance of these assets can reveal patterns and potential opportunities for diversification.
Gold and S&P 500: A Comparison in Investment Performance
When examining the investment performance of gold and the S&P 500, it’s important to consider both short-term and long-term perspectives. In some cases, gold may outperform the stock market during periods of economic downturn or global instability, while the S&P 500 may demonstrate resilience and growth over longer time horizons.
During economic crises or times of elevated volatility, gold often appeals to investors seeking to preserve capital and hedge against potential risks. The precious metal’s intrinsic value and limited supply make it a popular choice for those looking to safeguard their wealth.
On the other hand, the S&P 500 represents a broad index of U.S. stocks and offers investors exposure to a diverse range of companies across various sectors. The stock market has historically exhibited long-term growth, driven by innovation, technological advancements, and corporate profitability.
To illustrate the comparison between gold and the S&P 500, let’s take a closer look at their historical performance:
- In the 1970s, gold prices soared in response to the end of the Bretton Woods system and the stagflation crisis. This period witnessed a surge in demand for gold as investors sought a safe haven amidst economic uncertainty. Meanwhile, the S&P 500 experienced significant volatility during the same period.
- In 1999, the S&P 500 experienced a market bubble, driven by the dot-com boom. At this time, gold prices remained relatively flat.
- The 2008 financial crisis caused widespread economic turmoil and triggered a flight to safety. As investors sought refuge from the declining stock market, gold prices surged, reaching new highs. The S&P 500, however, experienced a sharp decline during this period.
- Throughout the European sovereign debt crisis in 2010-2012 and the tapering of quantitative easing by the Federal Reserve in 2013-2014, gold prices exhibited volatility. Meanwhile, the S&P 500 gradually recovered and continued its long-term upward trend.
- More recently, the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions have led to a surge in gold prices, reflecting increased investor demand for the safe haven asset. The S&P 500 experienced significant volatility in the initial stages of the pandemic but rebounded swiftly.
It’s important to note that each investment carries its own benefits and risks, and the decision to invest in gold or the stock market should align with an individual’s investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Click here to learn more about the relationship between gold prices and the S&P 500.
Notable Highs and Lows in Gold Prices
Certain events have played a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of gold prices throughout history. These events, ranging from geopolitical conflicts to economic crises, have undoubtedly left their mark on the precious metal’s value. Understanding these significant milestones can provide valuable insights into the dynamics of the gold market.
The Impact of the Bretton Woods System and the Stagflation Crisis
One notable period that saw a surge in gold prices was the 1970s. The demise of the Bretton Woods system in 1971, which fixed the value of the U.S. dollar to gold, marked a turning point. The disconnection of the dollar from gold led to increased inflationary pressures and a loss of confidence in fiat currencies. Consequently, investors sought the safe haven of gold, leading to a significant increase in its prices.
The stagflation crisis in the United States during the same decade further fueled the rise in gold prices. Stagflation, characterized by high inflation and stagnant economic growth, eroded the purchasing power of traditional assets. Investors turned to gold as a reliable store of value amidst the turmoil, driving its prices even higher.
The Dot-Com Bubble and the Great Recession
The dot-com bubble of the late 1990s and early 2000s had a contrasting impact on gold prices. The strong performance of the U.S. economy and the excessive optimism surrounding technology stocks caused gold prices to decline. Investors were drawn to the allure of the stock market, diverting attention and capital away from gold.
However, the tides turned in 2008 with the onset of the Great Recession. The financial crisis heightened fears of economic collapse and widespread market volatility. Amidst the uncertainty, gold regained its status as a safe haven. Investors flocked to gold as a secure asset, driving prices upward once again.
The European Sovereign Debt Crisis and Quantitative Easing
The European sovereign debt crisis, which unfolded between 2010 and 2012, had a substantial impact on gold prices. Fears of a potential collapse of the Eurozone and concerns over the stability of European economies intensified demand for gold. Investors sought refuge in the precious metal as a hedge against the turmoil in the region.
The subsequent years saw the tapering of quantitative easing programs by the Federal Reserve, which added another layer of complexity to gold prices. As the central bank gradually reduced its bond-buying activities, the uncertainty surrounding the future of monetary policy and the potential impact on the economy sparked volatility in gold prices.
The Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Geopolitical Tensions
The COVID-19 pandemic, which emerged in 2020, brought about a renewed surge in gold prices. The global health crisis disrupted economies and heightened uncertainties, prompting investors to seek the stability and security offered by gold. The pandemic underscored the importance of holding assets that can withstand economic shocks, leading to increased demand and higher gold prices.
Additionally, geopolitical tensions, such as trade disputes and political conflicts, have consistently influenced gold prices. Uncertainty and the perceived risk associated with these events have driven investors to flock to gold as a safe haven in times of turbulence.
Understanding the impact of these notable events on gold prices can provide key insights for investors. It highlights the role of gold as a safe haven and a store of value amidst economic uncertainties. To delve deeper into the dynamics of gold prices and glean valuable investment insights, CNBC provides in-depth analysis and expert opinions on recent trends in the gold market.
Image: Historical fluctuations in gold prices
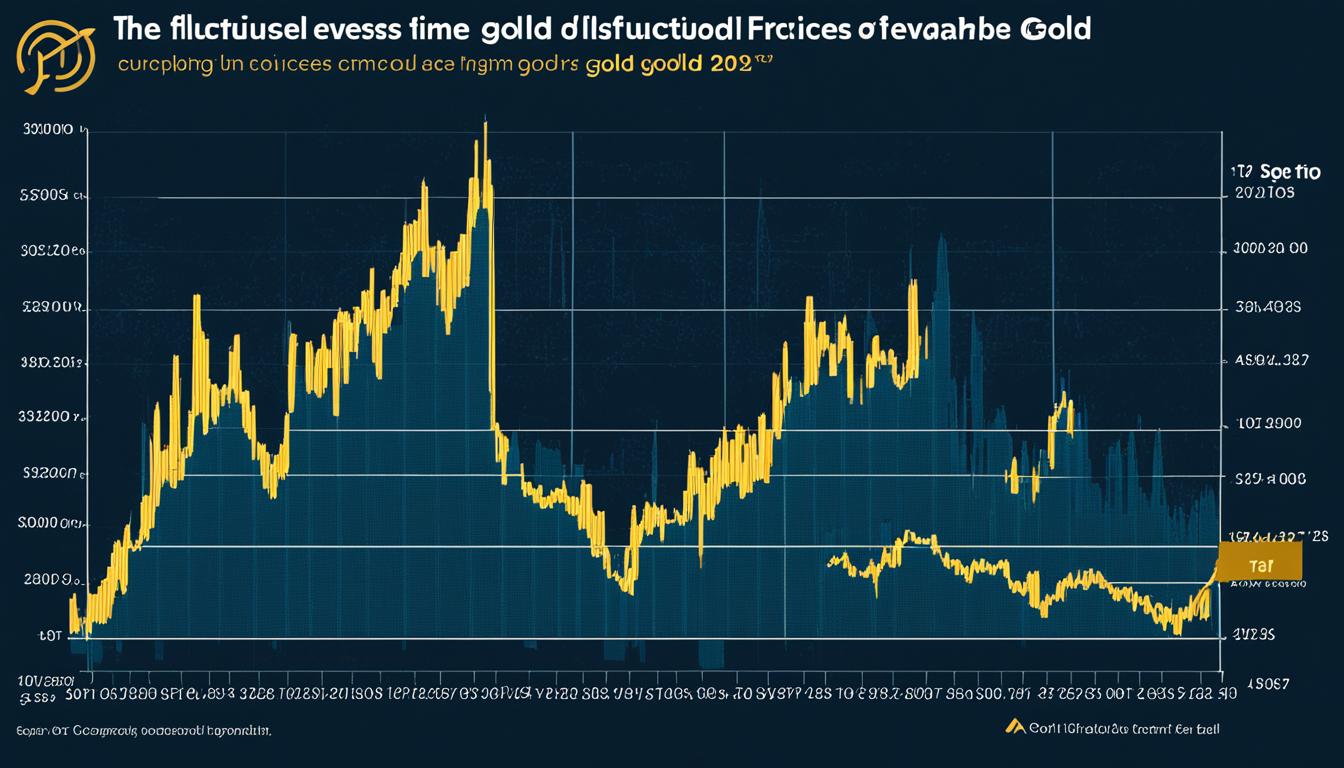
Factors Affecting the Price of Gold
When it comes to the price of gold, there are several factors that come into play. Understanding these factors can help investors make informed decisions and navigate the dynamic gold market.
Macroeconomic Conditions
The price of gold is closely tied to macroeconomic conditions, such as inflation and geopolitical tensions. In times of economic uncertainty or when there is a perceived threat to global stability, investors often turn to gold as a safe-haven asset. This increased demand can drive up the price of gold.
Supply and Demand
The limited supply of gold plays a significant role in its price. Gold is a finite resource, and the cost and complexity of mining and refining further contribute to its scarcity. Fluctuations in mining production, exploration activities, and government policies can impact the overall supply of gold, which in turn affects its price.
Currency Fluctuations
Gold is valued in relation to various currencies, and fluctuations in currency exchange rates can influence its price. When a particular currency weakens, investors may turn to gold as a hedge against currency depreciation, driving up demand and consequently raising the price of gold.
Mining Costs
The cost of mining and refining gold is another factor that influences its price. The expenses associated with extracting gold from the ground, including labor, equipment, and energy costs, can impact the overall supply of gold and therefore its price. Changes in mining technology and regulatory requirements can also affect mining costs and subsequently impact the price of gold.
In addition to these fundamental factors, gold’s status as a store of value and its unique qualities further contribute to its appeal as an investment. Its historical track record and potential to provide a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainties make it a popular choice among investors seeking diversification and wealth preservation.
Conclusion
Investing in gold offers numerous benefits for individuals looking to diversify their portfolios and protect their wealth from economic uncertainties. Gold has a long history of high performance and serves as a safe-haven asset during times of inflation and geopolitical risks. Its unique qualities, such as its scarcity and durability, make it an appealing investment option.
However, it is important to carefully consider the risks and drawbacks associated with gold investing. Personal financial goals and investing preferences should guide the decision to include gold in a portfolio. While gold can offer potential benefits, it should not dominate one’s investment strategy. Financial advisors typically recommend allocating no more than 5-10% of one’s total investment to gold.
Given the current economic uncertainties and the recent surge in gold prices, many investors may find it advantageous to consider adding gold to their investment strategy. Gold can provide a hedge against inflation and geopolitical risks, offering stability and preserving wealth in volatile markets. Whether through physical gold or various investment vehicles, incorporating gold into a well-rounded portfolio can offer investors an added layer of protection and potential long-term gains.




